AI That Simplifies Trade Compliance and Drives Growth
The Role of Process Automation in Customs Operations
-
Freya Jane
- Director of Customer's Success
Time has progressed, and customs trade has flourished with a 360-degree turnover. Global enterprises need timely goods clearance, correct documentation, and customs compliance. Automation transforms customs procedures. Process automation describes the customs declaration flow, which is easy to follow and suitable for every trader.
Technology and digital solutions can streamline customs management, improving efficiency, cost, compliance, and competitiveness. Process automation has a major impact on customs management and international trade.
What research says about international trade efficiency:
Efficiency is essential in the arena of international trade. Successful imports and exports are based on the timely clearance of products, proper documentation, and compliance with customs. On the other hand, even small delays in customs procedures might have a big impact.
A recent study conducted by Revenue found that
“A country’s exports can drop by 3.8% for every 10% rise in customs delays.“
This emphasises how crucial faster customs procedures are in order to guarantee seamless international trade, which is made possible by process automation. Let’s dive deep into understanding what process automation is and how it is helpful in international trade.
Understanding Process Automation
Process automation, meaning the method of utilising technology and software to either provide services or manufacture products, falls under the section of process automation. It includes the design and implementation of the system.
It is able to carry out these tasks automatically according to the rules or instructions that have been specified. Process automation solutions improve productivity, efficiency, accuracy, and time. Automating monotonous chores frees up human resources for strategic and value-added work.
How does process automation benefit businesses?
Businesses operating in a wide variety of sectors can reap numerous benefits from automating their processes. Here are several significant advantages:
Process automation increases Productivity and Efficiency
Processes automation expedites customs procedures, streamlines workflows, and eliminates manual labour. Customs officials can concentrate on more complicated matters by automating repetitive procedures, which raises productivity and improves overall trade transaction efficiency.
Time and money savings
Automating customs processes speeds up the clearance of products by reducing processing times. Businesses benefit financially from this expedited clearance process since it reduces holding and storage expenses related to delayed goods.
Increased accuracy and consistency
When processing documents and data pertaining to trade, automated methods guarantee a greater degree of accuracy and consistency. Automating data entry and processing reduces human error, which improves the dependability of customs processes.
Compliance and risk management
By constantly implementing rules and regulations, automation aids with compliance with regulatory standards. Furthermore, automated risk assessment technologies can quickly spot potential errors or shipment-related issues, freeing up authorities to concentrate on successfully reducing those risks.
Handling scalability and capacity
Automated systems are highly capable of accommodating variations in trade volumes with ease. They can manage higher transaction volumes without sacrificing effectiveness, guaranteeing the scalability and adaptability of customs operations to fluctuating workloads.
Better customer experience
Automation results in less paperwork, quicker processing times, and more seamless clearing procedures. For businesses engaged in international trade, this means a better experience that promotes favourable relationships and ongoing trade relationships.
Data visibility and analytics
Automation makes trade data and analytics more visible. Customs officials may make better decisions, spot trends, and streamline procedures with the aid of this data-driven strategy, which also improves performance and decision-making.
Adaptability and agility
Compared to manual procedures, automated systems are able to adjust to changes in trade rules, legislation, and technological advances more quickly. Because of its flexibility, customs operations are able to adjust quickly to changing trade conditions.
Satisfied and engaged employees
Automation relieves employees of tiresome duties, enabling them to concentrate on higher-value tasks. This increases job satisfaction and motivates workers to take on more critical and strategic duties.
Gaining a competitive edge
In the context of international trade, customs administrations can gain a competitive edge by utilising automation technologies. They can draw in more companies, make trade easier, and establish themselves as progressive participants in the global trade ecosystem by embracing innovation and efficiency.
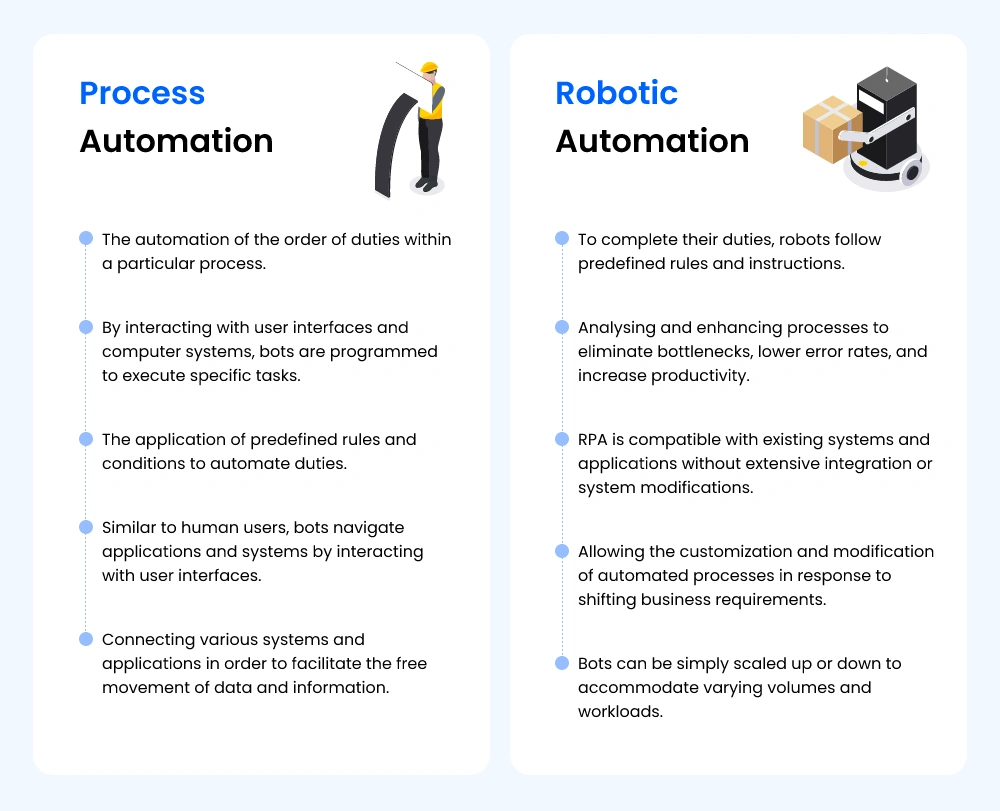
Difference between process automation and robotic automation
Process automation and robotic automation are two different terms or advancements that vary by company. Robotics and process automation streamline and optimise business operations. Both have important differences:
In a nutshell, process automation focuses on automating entire workflows or processes, whereas robotic automation focuses on automating repetitive, rule-based duties with software robots. Automating a process encompasses a broader range of technologies, whereas robotic automation employs software robots to replicate human actions and perform tasks.
Process automation of iCustoms
This blog explicitly discusses the process automation service of customs trading. It is a leading solution that allows customs brokers to manage their trading online via a single platform. The customs process automation sequence of iCustoms is fully AI-based and manages the customs operations of both import and export.
It has created an artificial intelligence-based service of intelligent document processing for the smart document automation of customs documents. This process is widely supported and useful for customs operators during customs clearance. Process automation, as in the form of IDP software, is a novel service that reads the documents and extracts the information.
This customs management service ensures that from registering until the submission of the customs, iCustoms is a complete package that will manage every step according to one’s needs. Customs business automation with iCustoms gives accurate HS code results with 99% accuracy in customs submission.
Intelligent document automation is a new path that is becoming famous globally regardless of its use in every field because of its features. But, in the customs world, iCustoms is the foremost organisation to provide this opportunity for smart documentation due to its intelligent automation service.
Summarising
International trade enterprises need efficient customs handling. Process automation can alter customs procedures, improving efficiency, cost, and compliance. Automation improves customs clearance, documentation, and compliance.
Customs process automation will grow with technology. Businesses must invest in automation technologies to compete globally. Automation helps organisations streamline customs procedures and expand globally.
Eager to optimise your customs operations? Join together with iCustoms today for cutting-edge automation solutions. Boost trade productivity and welcome a smooth international trade future. Get in touch with us right now to transform your customs procedures.
FAQs
What is process automation?
Process automation is using technology to carry out routine customs operations or processes with a minimum of human involvement. Through the automation of repetitive operations, it seeks to improve efficiency, decrease manual labour, and streamline processes.
What is automated data processing?
The term "automated data processing" describes the use of software and technology to handle, process, and alter data automatically—all without the need for human involvement.
What is the process automation approach?
The process automation method entails examining current processes, locating time-consuming or repetitive operations, and then putting technical solutions in place to automate these tasks.
What are the types of process automation?
Here are the four common types of process automation:
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
- Business Process Automation (BPA)
- Cognitive Automation
- Integration of Systems
